NEWS
Company News
Mechanical sealing auxiliary sealing material and selection
TIME:2023-02-17
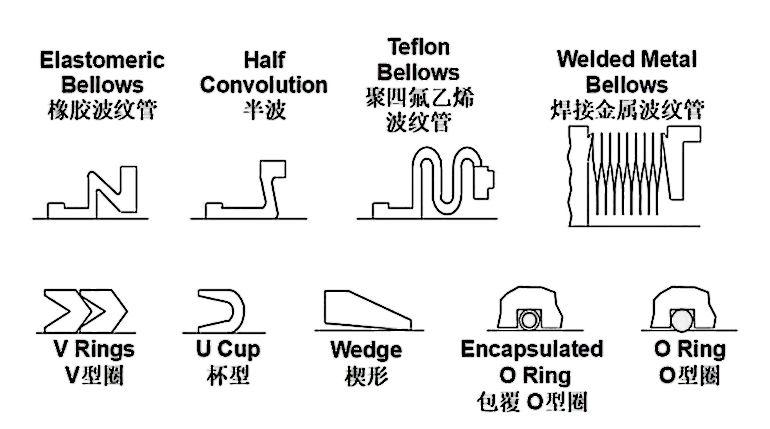
Auxiliary seal includes the sealing ring of moving and static ring, which are mostly made into O-ring, V-ring, rectangular ring, wedge ring or trapezoidal ring.
Their main functions are: to prevent the leakage between the moving ring and the rotating shaft and the static ring and the pressure cover; to compensate for the deflection and vibration of the sealing surface to ensure the good fit of the dynamic and static ring end surface.
The main materials of the auxiliary sealing ring are elastomers (such as rubber), plastics (such as tetrafluoroethylene), fibers (such as asbestos, carbon fiber), inorganic materials (such as expanded graphite) and metals (such as copper, aluminum, stainless steel, etc.).
The requirements for the physical and mechanical properties of the auxiliary sealing ring material are related to the sealing surface material.
1. Synthetic rubber
Rubber auxiliary seal ring is the most widely used auxiliary seal ring. Commonly used rubber sealing ring materials are nitrile rubber, fluorine rubber silicone rubber, neoprene rubber and so on.
(1) Nitrile rubber NBR nitrile rubber is the most commonly used kind of rubber. It is a copolymer of butadiene and acrylonitrile. According to the amount of acrylonitrile divided into several kinds: low acrylonitrile (nitrile-18), medium acrylonitrile (nitrile-26) and high acrylonitrile (nitrile-40). The higher the content of acrylonitrile, the better its oil resistance, tensile strength, hardness and wear resistance, water resistance, reduced air permeability. Subsequently, its solubility in the polar solvent increases, and its corrosion resistance is also affected. The elasticity and cold resistance will also deteriorate. Nitrile rubber is not resistant to flexion and has poor tear resistance. The content of acrylonitrile in the general nitrile rubber sealing ring is 26%~50%.
Nitrile rubber has excellent corrosion resistance to mineral oil, animal and plant fat, fat hydrocarbon, and is widely used to contact gasoline and other oil equipment. It can be resistant to alkali and non-oxidation dilute acid corrosion, not resistant to oxidative acid (such as nitric acid, chromic acid, etc.), aromatic hydrocarbons, lipid, ketone, ether, halogenated hydrocarbon and other corrosion.
Recently, hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) was developed, which is better than nitrile rubber. The use of temperature range is-40~150℃, oil resistance is better than nitrile rubber, hydrogen sulfide resistance is better than fluoro rubber, in 200℃ steam use is second only to ethylene propylene rubber.
(2) Fluorine rubber FPM fluorine rubber has the advantages of high temperature resistance, oil resistance and chemical corrosion resistance. In the concentrated sulfuric acid, nitric acid, phosphoric acid, caustic soda and other media can be used. However, as the temperature increases, the corrosion resistance rate decreases, and the highest use temperature is 200℃.
The most widely used fluorine rubber in China is the copolymer containing fluorine and olefin, mainly including fluorine-23 type and fluorine-26 type.
Type 23 fluorine rubber is an amorphous rubber copolymer made of vinylidene fluoride and ethylene trifluorinated chloride at room temperature and about 3.3MPa under pressure. Type 23 fluorine rubber is equivalent to foreign Kel-F fluorine rubber, which can be used for strong acid.
There are two kinds of type 26 fluorine rubber: fluorine rubber-26, an emulsion copolymer of vinylidene fluoride and hexafluoropropylene, equivalent to foreign Viton fluorine rubber; fluorine rubber-246 is a ternary copolymer of vinylidene fluoride, hexafluoropropylene and tetrafluoroethylene.
In recent years, perfluorinated rubber (FFKM perfluorinated polyelastomer) has been developed, which is equivalent to foreign Kalrez perfluorinated rubber. It has excellent anti-aging performance and no obvious aging phenomenon after 112 days at 260℃. The tensile strength remains about 90% of the original, which can be used continuously at 288℃ and briefly at 310℃. It has good oil resistance, wear resistance and corrosion resistance of mixed organic matter, but its expansion coefficient is nearly twice that of nitrile rubber (320 * 10-6 / K), and it is not suitable for use below zero degree.
(3) silicone rubber MVQ silicone rubber high temperature resistance and low temperature resistance are very good, the safe use of the temperature range is-70~200℃. In dilute sulfuric acid, hydrochloric acid, acetic acid, caustic soda, ethanol, mineral oil and other media, there is no obvious corrosion phenomenon. Silicone rubber is a polar polymer composed of dimethylsiloxane and other silicone monomer in the presence of acidic or alkaline catalyst. Silicone rubber has a very high thermal stability, but it has a polarity, easy to occur in the ionic cracking under the action of acid and base, so the corrosion resistance is poor. It is not suitable for petroleum system solvents (such as benzene, toluene, etc.), acetone, ketone, ether and other organic solvents. The breaking strength and elongation of silicone rubber are small (only 1 / 3 of nitrile rubber).
Recently, fluorosilicone rubber (MFQ) can be widely used in gasoline, petroleum oil products and solvents.
(4) Ethylene propylene rubber EPM ethylene propylene rubber is composed of the polymerization of ethylene and propylene, divided into binary and ternary copolymers. It is especially resistant to phosphorester hydraulic oil, ketone, alcohol solution and acid and alkali, and can withstand high pressure steam, weather resistance and ozone resistance. However, it expands in mineral oil and diester lubricants and therefore cannot be used in these media.
2. PTFE PTFE
PTFE has better heat resistance, oil resistance and corrosion resistance than general rubber. It is commonly used to make V-ring and wedge ring in mechanical sealing. PTFE plastic has greater stiffness, low elasticity and cold flow. The high expansion coefficient of PTFE varies greatly with temperature, especially with a peak at room temperature, which prevents its application in mechanical sealing. However, PTFE has a large range of use (-150~250℃), very low friction coefficient (f=0.05~0.1 at low speed) and self-lubrication, surface unbonding, good chemical stability, can resist to chloride, boron fluoride, high boiling point solvent, ketone, ester, ether, boiling nitric acid, royal water, sodium hydroxide, hydrofluoric acid, etc. The only ones that will erode PTFE are molten metals and fluorine at high pressure. Under load action, creep (i. e., cold flow) occurs at any temperature, over 8) 83, it will sublimate to produce toxic smoke.
3. Other materials
Other materials used as auxiliary seals are metal, filled polytetrafluoroethylene, expanded graphite (flexible graphite), asbestos, and rubber-plastic composites. These materials are mainly used in high-temperature occasions.
Their main functions are: to prevent the leakage between the moving ring and the rotating shaft and the static ring and the pressure cover; to compensate for the deflection and vibration of the sealing surface to ensure the good fit of the dynamic and static ring end surface.
The main materials of the auxiliary sealing ring are elastomers (such as rubber), plastics (such as tetrafluoroethylene), fibers (such as asbestos, carbon fiber), inorganic materials (such as expanded graphite) and metals (such as copper, aluminum, stainless steel, etc.).
The requirements for the physical and mechanical properties of the auxiliary sealing ring material are related to the sealing surface material.
1. Synthetic rubber
Rubber auxiliary seal ring is the most widely used auxiliary seal ring. Commonly used rubber sealing ring materials are nitrile rubber, fluorine rubber silicone rubber, neoprene rubber and so on.
(1) Nitrile rubber NBR nitrile rubber is the most commonly used kind of rubber. It is a copolymer of butadiene and acrylonitrile. According to the amount of acrylonitrile divided into several kinds: low acrylonitrile (nitrile-18), medium acrylonitrile (nitrile-26) and high acrylonitrile (nitrile-40). The higher the content of acrylonitrile, the better its oil resistance, tensile strength, hardness and wear resistance, water resistance, reduced air permeability. Subsequently, its solubility in the polar solvent increases, and its corrosion resistance is also affected. The elasticity and cold resistance will also deteriorate. Nitrile rubber is not resistant to flexion and has poor tear resistance. The content of acrylonitrile in the general nitrile rubber sealing ring is 26%~50%.
Nitrile rubber has excellent corrosion resistance to mineral oil, animal and plant fat, fat hydrocarbon, and is widely used to contact gasoline and other oil equipment. It can be resistant to alkali and non-oxidation dilute acid corrosion, not resistant to oxidative acid (such as nitric acid, chromic acid, etc.), aromatic hydrocarbons, lipid, ketone, ether, halogenated hydrocarbon and other corrosion.
Recently, hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR) was developed, which is better than nitrile rubber. The use of temperature range is-40~150℃, oil resistance is better than nitrile rubber, hydrogen sulfide resistance is better than fluoro rubber, in 200℃ steam use is second only to ethylene propylene rubber.
(2) Fluorine rubber FPM fluorine rubber has the advantages of high temperature resistance, oil resistance and chemical corrosion resistance. In the concentrated sulfuric acid, nitric acid, phosphoric acid, caustic soda and other media can be used. However, as the temperature increases, the corrosion resistance rate decreases, and the highest use temperature is 200℃.
The most widely used fluorine rubber in China is the copolymer containing fluorine and olefin, mainly including fluorine-23 type and fluorine-26 type.
Type 23 fluorine rubber is an amorphous rubber copolymer made of vinylidene fluoride and ethylene trifluorinated chloride at room temperature and about 3.3MPa under pressure. Type 23 fluorine rubber is equivalent to foreign Kel-F fluorine rubber, which can be used for strong acid.
There are two kinds of type 26 fluorine rubber: fluorine rubber-26, an emulsion copolymer of vinylidene fluoride and hexafluoropropylene, equivalent to foreign Viton fluorine rubber; fluorine rubber-246 is a ternary copolymer of vinylidene fluoride, hexafluoropropylene and tetrafluoroethylene.
In recent years, perfluorinated rubber (FFKM perfluorinated polyelastomer) has been developed, which is equivalent to foreign Kalrez perfluorinated rubber. It has excellent anti-aging performance and no obvious aging phenomenon after 112 days at 260℃. The tensile strength remains about 90% of the original, which can be used continuously at 288℃ and briefly at 310℃. It has good oil resistance, wear resistance and corrosion resistance of mixed organic matter, but its expansion coefficient is nearly twice that of nitrile rubber (320 * 10-6 / K), and it is not suitable for use below zero degree.
(3) silicone rubber MVQ silicone rubber high temperature resistance and low temperature resistance are very good, the safe use of the temperature range is-70~200℃. In dilute sulfuric acid, hydrochloric acid, acetic acid, caustic soda, ethanol, mineral oil and other media, there is no obvious corrosion phenomenon. Silicone rubber is a polar polymer composed of dimethylsiloxane and other silicone monomer in the presence of acidic or alkaline catalyst. Silicone rubber has a very high thermal stability, but it has a polarity, easy to occur in the ionic cracking under the action of acid and base, so the corrosion resistance is poor. It is not suitable for petroleum system solvents (such as benzene, toluene, etc.), acetone, ketone, ether and other organic solvents. The breaking strength and elongation of silicone rubber are small (only 1 / 3 of nitrile rubber).
Recently, fluorosilicone rubber (MFQ) can be widely used in gasoline, petroleum oil products and solvents.
(4) Ethylene propylene rubber EPM ethylene propylene rubber is composed of the polymerization of ethylene and propylene, divided into binary and ternary copolymers. It is especially resistant to phosphorester hydraulic oil, ketone, alcohol solution and acid and alkali, and can withstand high pressure steam, weather resistance and ozone resistance. However, it expands in mineral oil and diester lubricants and therefore cannot be used in these media.
2. PTFE PTFE
PTFE has better heat resistance, oil resistance and corrosion resistance than general rubber. It is commonly used to make V-ring and wedge ring in mechanical sealing. PTFE plastic has greater stiffness, low elasticity and cold flow. The high expansion coefficient of PTFE varies greatly with temperature, especially with a peak at room temperature, which prevents its application in mechanical sealing. However, PTFE has a large range of use (-150~250℃), very low friction coefficient (f=0.05~0.1 at low speed) and self-lubrication, surface unbonding, good chemical stability, can resist to chloride, boron fluoride, high boiling point solvent, ketone, ester, ether, boiling nitric acid, royal water, sodium hydroxide, hydrofluoric acid, etc. The only ones that will erode PTFE are molten metals and fluorine at high pressure. Under load action, creep (i. e., cold flow) occurs at any temperature, over 8) 83, it will sublimate to produce toxic smoke.
3. Other materials
Other materials used as auxiliary seals are metal, filled polytetrafluoroethylene, expanded graphite (flexible graphite), asbestos, and rubber-plastic composites. These materials are mainly used in high-temperature occasions.
Previous:Relevant knowledge about the V-circle
Next:About the characteristics of the hard metal carbide sealing ring sheet
+86-0335-8085559
Junming (Hebei) Machinery and Equipment Manufacturing Co., Ltd.
Address:No.1 Huaihe Road, Qinhuangdao Economic and Technological Development Zone
Domestic:+86-0335-3066990
Overseas:+86-0335-8085559
Domestic:info@junmingmeco.com
Overseas:sales@junmingmeco.com
Website:www.junmingmeco.com
-

官方微信


 Recommendation
Recommendation

